

Understanding SPIGFD
On this page

Olive, a former INCRELEX patient, at age 18
IGF-1 Is an Essential Hormone for Growth
The GH–IGF-1 Relationship
GH is secreted from the pituitary gland and binds to the GH receptor (GHR) in many tissues, including the growth plate and the liver.1,3

The Role of GH and IGF-1 to Promote Growth1,3,4
Primary IGF-1 Deficiency Leads to Growth Failure
When Does Primary IGFD Become Severe Primary IGFD?
- height standard deviation score (SDS) ≤ -3.0
- basal IGF-1 SDS ≤ -3.0
- normal or elevated GH

Disruption of Growth in Primary IGF-1 Deficiency1,3
What Causes SPIGFD?
- GHR gene mutations or deletions
- GHR abnormalities
- Post-GHR signaling pathway defects
- Bioinactive IGF-1
- Primary defects of synthesis and action of IGF-1
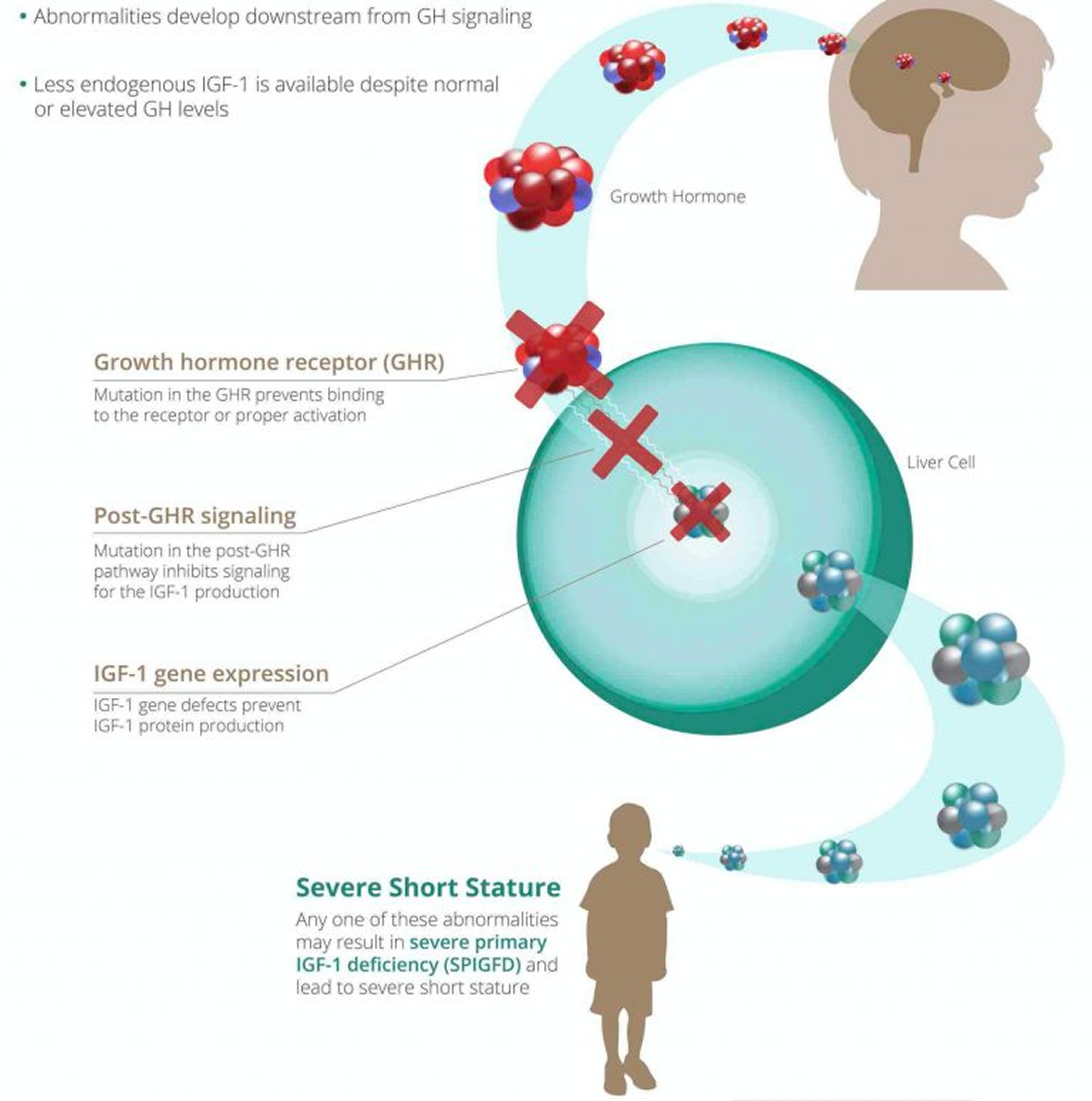
How Deficiency in IGF-1 Levels Develops into SPIGFD
Indication and important safety information
INCRELEX® (mecasermin) is indicated for the treatment of growth failure in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older with severe primary IGF-1 deficiency* (IGFD), or with hormone (GH) gene deletion who have developed neutralizing antibodies to GH.
Limitations of use: INCRELEX is not a substitute to GH for approved GH indications. INCRELEX is not indicated for use in patients with secondary forms of IGFD, such as GH deficiency, malnutrition, hypothyroidism, or chronic treatment with pharmacologic doses of anti-inflammatory steroids.
*Severe primary IGF-1 deficiency (IGFD) is defined by height standard deviation score ≤ -3.0 and basal IGF-1 standard deviation score ≤ -3.0 and normal or elevated GH.
Important safety information
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity: to mecasermin (rhIGF-1), any of the inactive ingredients in INCRELEX, or who have experienced a severe hypersensitivity to INCRELEX. Allergic reactions have been reported, including anaphylaxis requiring hospitalization.
- Closed Epiphyses
- Malignant Neoplasia in pediatric patients with malignant neoplasia or a history of malignancy.
Warning and precautions
- Hypoglycemia: INCRELEX should be administered 20 minutes before or after a meal or snack and should not be administered when the meal or snack is omitted. Glucose monitoring and INCRELEX dose titration are recommended until a well-tolerated dose is established and as medically indicated.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Funduscopic examination is recommended at the initiation of and periodically during the course of therapy.
- Lymphoid Tissue Hypertrophy: Patients should have periodic examinations to rule out potential complications.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients receiving products indicated to treat growth failure and/or short stature, including INCRELEX. Carefully evaluate any pediatric patient with the onset of a limp or hip/knee pain during INCRELEX therapy.
- Progression of Scoliosis: Patients with a history of scoliosis, treated with INCRELEX, should be monitored.
- Malignant Neoplasia: There have been postmarketing reports of malignant neoplasia in pediatric patients who received treatment with INCRELEX. It is unknown whether there is any relationship between Increlex therapy and new occurrences of neoplasia. The tumors were observed more frequently in patients who received INCRELEX at higher than recommended doses or at doses that produced serum IGF-1 levels above the normal reference ranges for age and sex. Monitor all patients receiving INCRELEX carefully for development of neoplasms. If malignant neoplasia develops, discontinue INCRELEX treatment.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preserved Solution: Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs. Use of INCRELEX in infants is not recommended.
Adverse reactions
Common adverse reactions include hypoglycemia, local and systemic hypersensitivity, and tonsillar hypertrophy.
To report a suspected adverse event related to INCRELEX, contact Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-224-0233 or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at www.fda.gov/safety/Medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information for more information.
References
- Backeljauw PF, Chernausek SD. Treatment of severe IGF-1 deficiency with recombinant human IGF-1 (mecasermin). Curr Med Lit Growth. 2009;23:69-95.
- Cohen J, Blethen S, Kuntze J, et al. Managing the child with severe primary insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency (IGFD): IGFD diagnosis and management. Drugs R D. 2014;141:25-29.
- Kemp SF. Insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency in children with growth hormone insensitivity: current and future treatment options. BioDrugs. 2009;233:155-163.
- Fintini D, Brufani C, Cappa M. Profile of mecasermin for the long-term treatment of growth failure in children and adolescents with severe primary IGF-1 deficiency. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009;53:553-559.
- Le Roith D, Scavo L, Butler A. What is the role of circulating IGF-I? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;122:48-52.
- Savage MO, Burren CP, Rosenfeld RG. The continuum of growth hormone IGF-I axis defects causing short stature: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010;726:721-728.
- INCRELEX. Package insert. Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc;2023.
Indication and important safety information
INCRELEX® (mecasermin) is indicated for the treatment of growth failure in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older with severe primary IGF-1 deficiency* (IGFD), or with hormone (GH) gene deletion who have developed neutralizing antibodies to GH.
Limitations of use: INCRELEX is not a substitute to GH for approved GH indications. INCRELEX is not indicated for use in patients with secondary forms of IGFD, such as GH deficiency, malnutrition, hypothyroidism, or chronic treatment with pharmacologic doses of anti-inflammatory steroids.
*Severe primary IGF-1 deficiency (IGFD) is defined by height standard deviation score ≤ -3.0 and basal IGF-1 standard deviation score ≤ -3.0 and normal or elevated GH.
Important safety information
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity: to mecasermin (rhIGF-1), any of the inactive ingredients in INCRELEX, or who have experienced a severe hypersensitivity to INCRELEX. Allergic reactions have been reported, including anaphylaxis requiring hospitalization.
- Closed Epiphyses
- Malignant Neoplasia in pediatric patients with malignant neoplasia or a history of malignancy.
Warning and precautions
- Hypoglycemia: INCRELEX should be administered 20 minutes before or after a meal or snack and should not be administered when the meal or snack is omitted. Glucose monitoring and INCRELEX dose titration are recommended until a well-tolerated dose is established and as medically indicated.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Funduscopic examination is recommended at the initiation of and periodically during the course of therapy.
- Lymphoid Tissue Hypertrophy: Patients should have periodic examinations to rule out potential complications.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients receiving products indicated to treat growth failure and/or short stature, including INCRELEX. Carefully evaluate any pediatric patient with the onset of a limp or hip/knee pain during INCRELEX therapy.
- Progression of Scoliosis: Patients with a history of scoliosis, treated with INCRELEX, should be monitored.
- Malignant Neoplasia: There have been postmarketing reports of malignant neoplasia in pediatric patients who received treatment with INCRELEX. It is unknown whether there is any relationship between Increlex therapy and new occurrences of neoplasia. The tumors were observed more frequently in patients who received INCRELEX at higher than recommended doses or at doses that produced serum IGF-1 levels above the normal reference ranges for age and sex. Monitor all patients receiving INCRELEX carefully for development of neoplasms. If malignant neoplasia develops, discontinue INCRELEX treatment.
- Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preserved Solution: Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs. Use of INCRELEX in infants is not recommended.
Adverse reactions
Common adverse reactions include hypoglycemia, local and systemic hypersensitivity, and tonsillar hypertrophy.
To report a suspected adverse event related to INCRELEX, contact Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-855-224-0233 or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at www.fda.gov/safety/Medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information for more information.
References
- Backeljauw PF, Chernausek SD. Treatment of severe IGF-1 deficiency with recombinant human IGF-1 (mecasermin). Curr Med Lit Growth. 2009;23:69-95.
- Cohen J, Blethen S, Kuntze J, et al. Managing the child with severe primary insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency (IGFD): IGFD diagnosis and management. Drugs R D. 2014;141:25-29.
- Kemp SF. Insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency in children with growth hormone insensitivity: current and future treatment options. BioDrugs. 2009;233:155-163.
- Fintini D, Brufani C, Cappa M. Profile of mecasermin for the long-term treatment of growth failure in children and adolescents with severe primary IGF-1 deficiency. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009;53:553-559.
- Le Roith D, Scavo L, Butler A. What is the role of circulating IGF-I? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;122:48-52.
- Savage MO, Burren CP, Rosenfeld RG. The continuum of growth hormone IGF-I axis defects causing short stature: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010;726:721-728.
- INCRELEX. Package insert. Eton Pharmaceuticals, Inc;2023.
